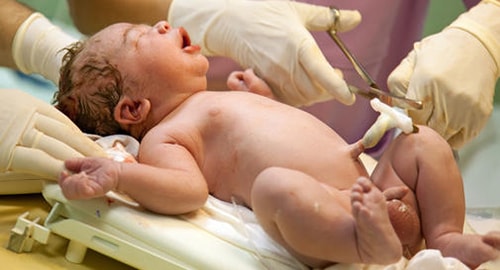
 Cord tissue is easy and painless to collect at the time of birth
Cord tissue is easy and painless to collect at the time of birth
Cord tissue, or Wharton’s jelly, is the insulating tissue surrounding the two arteries and one vein found in the umbilical cord. It contains fats, white cells and, more importantly, a great number of stem cells. These stem cells were discovered in the 1990s, and their potential in regenerative medicine was quickly realized.
As banking cord blood was already an established service by the time cord tissue's stem cells were discovered, it was easy for many cord blood banks to also start collecting and preserving the umbilical cord tissue. Cord tissue banking is the service of collecting, preparing and cryo-preserving the cord tissue for potential future therapeutic use.
It's important to note that umbilical cord blood and cord tissue are rich in two distinct types of stem cells. Both types of stem cells play key roles in regenerative medicine, and each works in its own way.
Read about how cord blood and cord tissue compare.
Cord tissue's role in regenerative medicine
There are many different types of stem cells present in cord tissue, and they all have different potential uses. There are epithelial (ep-i-thee-lee-al) and endothelial (en-do-thee-lee-al) stem cells, but cord tissue is mainly rich in mesenchymal (meh-sen-ki-mal) stem cells, or MSCs. MSCs are the precursors to the cells of the nervous system, sensory organs, circulatory tissues, skin, bone, cartilage and more.
MSCs are powerful stem cells that help repair and heal the body in different ways than cord blood. Cord tissue stem cells have many functions including the ability to inhibit inflammation following tissue damage, secrete growth factors that aid in tissue repair and differentiate into many cell types including neural cells, bone cells, fat cells and cartilage.
MSCs are currently being investigated in hundreds of clinical trials. While the research is in its early stages, the possibilities are promising.
| Clinical trials currently underway |
| ALS (Lou Gehrig’s Disease) |
Lupus |
| Alzheimer’s |
Muscular Dystrophy |
| Aplastic anemia |
Multiple Sclerosis |
| Myocardial infarction |
Cardiomyopathy |
| Osteoarthritis |
Cartilage repair |
| Parkinson’s |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Crohn’s Disease |
Spinal cord injuries |
| Connective tissue diseases & damage |
Stroke |
| Diabetes |
Traumatic optic neuropathy |
| Liver failure |
Ulcerative colitis |
| Lung injury |
Wounds, burns, ulcers |
Read more about treatments using stem cells.
How does cord tissue banking work?
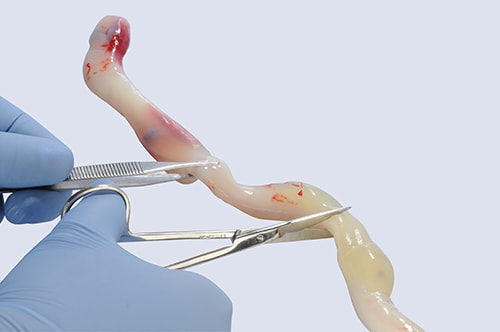 Approx. 6" of the umbilical cord will be collected when cord tissue banking
Approx. 6" of the umbilical cord will be collected when cord tissue banking
The cord tissue banking process begins with the procurement of approximately six inches of the umbilical cord at time of birth. This is performed after the placenta has been delivered, the umbilical cord has been cut and the umbilical cord blood has been collected. The segment of the cord is cleansed and placed in a container containing antibiotics for transportation to the laboratory. The cord tissue collection is safe and may be performed in both vaginal and cesarean-section (C-section) births. The container will be transported along with the cord blood for immediate processing at the cord blood laboratory.
Our cord tissue banking service
At Cryo-Cell International, cord tissue is cryo-preserved in its natural environment. If needed, the stem cells are then extracted immediately before their expected use. This provides the most flexibility for the future use of cells found in the cord tissue. Other cord blood banks extract the stem cells from the tissue through enzymatic digestion before cryo-preservation.43 By waiting to extract the stem cells, our method preserves multiple cell types that may be beneficial in future cell therapies for your baby and family.
The cryo-preservation processing method used by Cryo-Cell International has been independently acknowledged as the best. According to scientific data published in the October 2015 issue of Placenta, cord tissue that has undergone minimal manipulation "appears to be the optimal solution for umbilical cord tissue MSCs storage for future clinical use because the cryo-preservation of the previously isolated and expanded cells using unstandardized protocols can be considered non-compliant in relation to future accepted standards."
| Feature |
Benefits |
| Cord tissue undergoes minimal manipulaton prior to storage |
Preserves multiple cell types for potential future therapies including mesenchymal stem cells, endothelial cells, perivascular cells, growth factors & proteins, and epithelial cells. |
| Cord tissue is processed post-preservation |
Provides the best possible chance the cord tissue stem cells will be acceptable if needed for a wide range of treatments and clinical applications. Leaves the opportunity for the processing method to comply with any future FDA guidelines. |
| Cord tissue is stored in up to 6 vials |
Allows the potential for multiple therapeutic treatments, and samples can be thawed independently at different times. |
Why should I bank cord tissue and cord blood?
The large number of stem cells collected from cord tissue have the ability to regenerate and differentiate into many different types of cells; therefore, they can potentially be used to treat more conditions than cord blood can treat alone. MSCs are increasingly being studied in regenerative medicine for a wide range of conditions including heart and kidney disease, ALS, wound healing and autoimmune diseases. In addition, many new studies using allogeneic MSCs show that regenerative medicine is most effective with a mix of stem cell types (simulating the team work taking place within our organs and tissues). MSCs have been used in clinical trials to complement the cord blood stem cells in the same transplant.41, 42
Umbilical cord tissue banking is now commonplace, with over 60 percent of Cryo-Cell’s customers electing to store both their babies' cord blood and their babies' cord tissue. Read more about why you should bank cord blood and cord tissue.
Want to learn more? We are here to answer any question you may have and can send you any information about cord tissue banking that you need.
In order to preserve more types and quantity of umbilical cord stem cells and to maximize possible future health options, Cryo-Cell’s umbilical cord tissue service provides expectant families with the opportunity to cryogenically store their newborn’s umbilical cord tissue cells contained within substantially intact cord tissue. Should umbilical cord tissue cells be considered for potential utilization in a future therapeutic application, further laboratory processing may be necessary. Regarding umbilical cord tissue, all private blood banks’ activities for New York State residents are limited to collection, processing, and long-term storage of umbilical cord tissue stem cells. The possession of a New York State license for such collection, processing and long-term storage does not indicate approval or endorsement of possible future uses or future suitability of these cells.